Listen to This Article:
As you cruise your grocery store aisles searching for the perfect ingredients for your next cooking project, buzzwords on packaging try to grab your attention. Two terms, “organic” and “sustainable” appear on everything from milk and cereal to fresh produce.
The 2023 US market for organic products was worth approximately $70 billion, which is a surprising 20% of the U.S. Food Gross Domestic Product. At first glance, you might think organic and sustainable mean the same thing. In truth, they mean different, though related, things. So what’s the difference?
How Does Organic Agriculture Relate to Sustainable Agriculture?
Though they are similar in impact and effect, organic agriculture is a specific growing prescription, while sustainable agriculture is more of a philosophical approach to agriculture.
What’s the difference between Organic and Sustainable Agriculture?
| Organic Agriculture | Sustainable Agriculture |
|---|---|
|
|
For example, crop rotation and the use of animal manure as fertilizer are both organic and sustainable agricultural practices.
However, organic farming isn’t always sustainable. For example, organic farmers could grow their crops under artificial lights or with heat to extend their season. This would meet the criteria for organic labeling, but wouldn’t be considered sustainable.
As another example, large-scale organic farms often grow the same row crops year after year. If those farms don’t responsibly replace nutrients after harvest, they may deplete soil health over time. Such farms could be considered organic, but not sustainable in the long term.
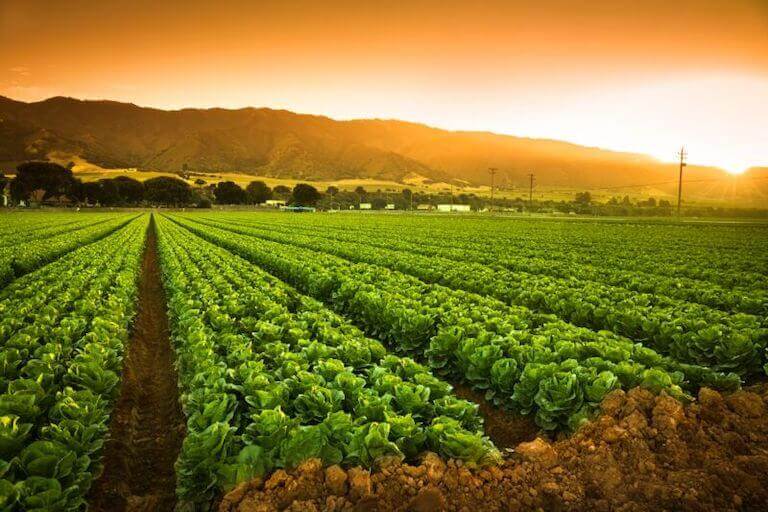

Organic farms may not necessarily be “sustainable.” They may use fossil fuel mechanization, artificial lights, intensive, large-scale row cropping, and more.
In addition, farm products, including organic produce, are often shipped far from their source farm. Transporting food by truck or train vastly increases the resources used to get it to market. For example, an organic tomato grown in California’s Central Valley and shipped to a grocery store in Boston is less sustainable than a tomato grown in Vermont and shipped to Boston because it uses far more fossil fuel resources to reach its end consumer.
These products could be labeled organic, but their use of resources would not be considered “sustainable.”
Let’s take a closer look at what makes agricultural practices specifically organic or sustainable.
What Is Organic Agriculture?
Organic agriculture is a farming method that uses all-natural and non-toxic growing practices.
Farmers whose products are certified organic can only use certain types of amendments, fertilizers, and other items to grow their crops, control pests, and harvest, process, and package their produce.
The term “organic” on food packaging and labels is a regulated, trademarked term.
What are “amendments?”
Growing plants in soil uses up nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and minerals. Farmers replace these important plant foods with supplements, which are often referred to as soil “amendments.” Organic farmers must use organic-approved fertilizers or practices to replace soil fertility, like animal manures, aged compost, bone meal, kelp powder, activated charcoal, or lime. They can also amend their soil by growing a cover crop and tilling it into the soil to compost in place.
What Does Organic Mean on a Label?
Organic generally means that the food was produced without harmful, synthetic chemicals or genetic modification. Many of the chemicals used in conventional agriculture are known to cause health problems in farm workers and consumers.
Choosing products labeled “organic” means that you are buying food that has not been treated with harmful chemicals, and from farmers who must care for their soil health.
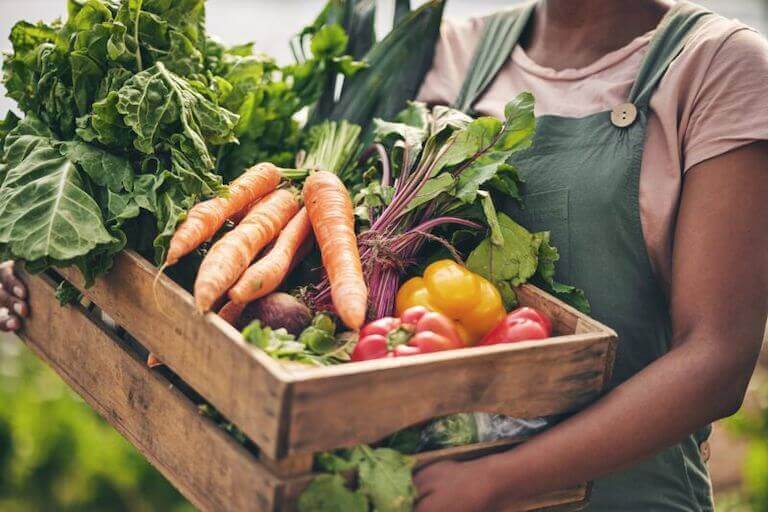

Organic produce is grown without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides.
Many organic certifications exist in the US, but in 2000, the USDA released national regulations for labeling organic products. The USDA awards the organic label to produce that is grown along the following guidelines.
Soil Management
Organic farms must rotate their crops to maintain soil nutrients. And instead of using unauthorized synthetic fertilizers, farmers must add nutrition to the soil using animal waste or certified products. Cover crops and tilling practices are also used.
Pesticides
Farmers growing organic crops must maintain their products without the use of chemical pesticides or herbicides. This means they need to rely on a list of allowable alternative products or use Integrated Pest Management (IPM). This practice involves managing insect habitat, introducing natural predators of pests, and using non-toxic pesticides and herbicides.
Organic Seeds
To attain organic labeling, farmers must grow their crops from certified organic seeds. This means that the plants that grew the seeds were also grown organically.
No Genetic Engineering
Changing the genes of crops with lab practices is a newer technique for agriculture. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are plants or animals whose genes have been altered or added to with technology.
Proponents say GMOs have the potential to revolutionize agriculture by increasing yields or reducing a crop’s susceptibility to pests. However, critics worry about the unforeseeable ecological and human health consequences of growing genetically modified plants.
Organic foods cannot be altered using genetic engineering or ionizing radiation. This means that foods labeled as organic are inherently free of GMOs.
The USDA also awards organic labels to dairy, animal, and multi-ingredient products. Organic animal products are raised without hormones.

The USDA Organic label means the farmers who produced the food didn’t use synthetic pesticides or fertilizers and took steps to preserve soil health. On multi-ingredient products, it means 95% of the ingredients are organic.
To use the “USDA Organic” green circle label, a multi-ingredient product must have a minimum of 95% organic ingredients. Farmers may also use additional organic certifiers, such as Oregon Tilth or California Certified Organic Farmers, which may have different labeling requirements.
What Is Sustainable Agriculture?
Sustainability is all about growing food without depleting or damaging natural resources. Unlike with organic agriculture, there is no national program of certification or labeling for sustainability. However, many independent organizations have established sustainability standards and offer certification. Examples include Friend of the Earth and Leading Harvest.
To be considered sustainable, farmed foods must at a minimum:
- Rely on natural, local resources as much as possible for soil amendments. Examples might be manures, cover crops, or compost from your own or nearby farms.
- Reduce transportation to a minimum. Buying a head of lettuce from the local farm down the road would be more sustainable than purchasing lettuce from the grocery store. Grocery store produce has often traveled thousands of miles in refrigerated trucks or trains using large amounts of non-renewable fuel.
- Minimize energy use for production. For example, sun-grown crops would be considered more sustainable than crops grown under electric lights.
- Replace the nutrients taken from the soil using natural, local sources. On-site composting of plant waste and maintaining soil fertility by cover cropping and practicing crop rotation are some examples.
- Support biodiversity.
- Be financially stable.
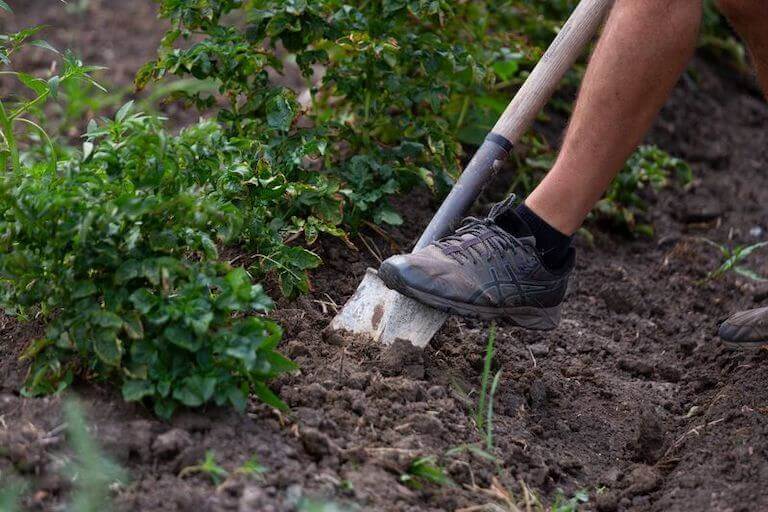

Sustainable agriculture focuses on using less energy, selling farm products locally, and improving the health of the environment.
In the bigger picture, farmers practicing sustainable agriculture work to maintain their soil health, and support the ecological integrity of their local environment.
Types of Sustainable Agriculture
Traditional cultures around the world have practiced types of sustainable agriculture throughout human history. But our modern agricultural systems have lost sight of their traditional roots in the name of mass production.
Several modern sustainable agriculture philosophies have emerged in the last 60 years. They attempt to find creative ways to produce the food we need as a society while preserving our future. Each uses the principles of ecology as a guide. Here are a few examples.
- Permaculture is a design strategy that intends to recreate natural ecological processes on the farm. Nutrient cycling, taking advantage of natural resources on-site or nearby, working with the seasons, and creating resilience are principles of Permaculture design that may be used on a farm.
- Agroecology is a philosophy of viewing and managing farms as ecosystems that are part of their surrounding environment. Creating relationships with nearby natural areas, using Integrated Pest Management (IPM), and no-till agriculture are examples of agroecology.
- Regenerative agriculture is a philosophy of growing food in a way that gives more back to the land and society than it takes. The key primary task is closing “energy loops” so that producing food and other resources doesn’t drain the ecological bank account but makes ongoing deposits.
The hope of sustainable agriculture is that humankind can continue growing food without depleting the soil’s fertility or polluting the environment in the long term.
Farm-to-Table: A Way to Choose Organic and Sustainable Food
For aspiring chefs, the food you cook for yourself and your diners can be both organic and sustainable. Choosing your ingredients with this in mind can be a simple way for your eating habits to care for the environment.
The easiest way to support and encourage organic and sustainable agriculture is to source your ingredients from local farms that adhere to both organic guidelines and sustainability principles. This practice is often called “farm-to-table” cuisine. The farm-to-table movement encourages people to eat close to home, to know their farmers, and to enjoy seasonal eating.
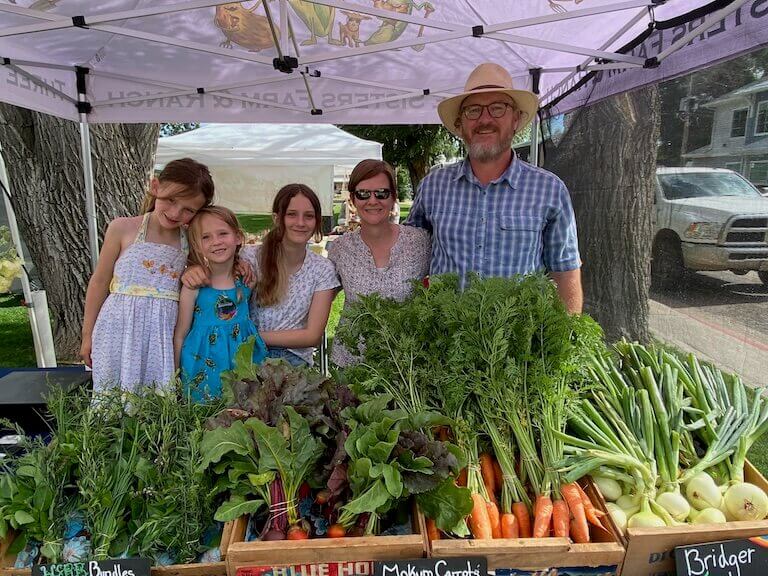

Support organic and sustainable agriculture practices by buying from your local farmer.
When you buy your ingredients from nearby farms, you naturally buy seasonal produce, which is grown in the optimal conditions for that plant. This ensures that your choice of produce isn’t wasting energy.
And beyond the environmental benefits of farm-to-table eating that you can feel good about, the food usually tastes much better. Food that was grown to tolerate long-distance transport across the country can’t compete with the succulent freshness of local, farm-grown veggies!
Boulder Campus Escoffier Chef Instructor Steven Nalls, who owns and operates Three Sisters Farm and Ranch in Wellington, Colorado commented: “I’d always gardened and I knew that the flavor is way different from the tomato on the vine in your backyard as opposed to the grocery store.” It brings to mind the famous line from Guy Clark: “There’s only two things that money can’t buy, and that’s true love and homegrown tomatoes.”
Other ways you can source organic or sustainable foods include:
- Attend farmers’ markets nearby and talk to the vendors to learn about how they produce their food. Support those farmers who provide organic, sustainable, local, and seasonal foods.
- Build relationships with farmers who use practices of which you approve.
Find Your Farm-to-Table Niche at Culinary School
Restaurants everywhere are embracing the Farm-to-Table trend. Diners love enjoying bespoke, one-time seasonal dishes made with luscious farm-fresh ingredients, like bruschetta on crusty Italian bread, or a warming carrot-ginger soup with a microgreen garnish.
If sustainable farming is important to you and you dream of becoming a chef who can be creative with the bounty of the season, why not consider attending culinary school at Escoffier?
Some of our diploma and degree programs include Farm-to-Table coursework, which teaches our culinary students how to bring the magic of farm-fresh products to the restaurant kitchen.
Chef Instructor Steven Nalls described part of the Farm-to-Table coursework in a recent interview: “We talk about sustainability and utilizing our resources appropriately not only in agriculture and what we’re sourcing but in the kitchen as well. We go through some whole animal usage and we focus on the whole vegetable as well. Don’t just throw those carrot tops away, find a way to turn those into a value-added scenario.”
Reach out to our admissions department to learn more about program options and ways to finance your culinary education.
IF YOU ENJOYED THIS ARTICLE ABOUT ORGANIC AND SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE, CONSIDER READING THESE ARTICLES NEXT:
- What Is a Plant-Based Diet?
- Michelin Green Star: Most Sustainable Restaurants in the U.S.
- What Is Carbon Neutral and Why Does it Matter to the Food Industry?
This article was originally published on January 30, 2014, and has since been updated.